|
Jinat Jahan Khan Movements in the stock market have been found to have a major impact on the economy. Changes in share prices can directly affect the real economy. A fall in share prices can lead to an economic crisis. The stock market crash of 1929 which led to the great depression of the 1930s can be cited as an example in this regard. Also, the downfall in stock prices from 2008 to 2009 in the U.S and then subsequently in the whole west created rifts in the real economy which caused the long recession. 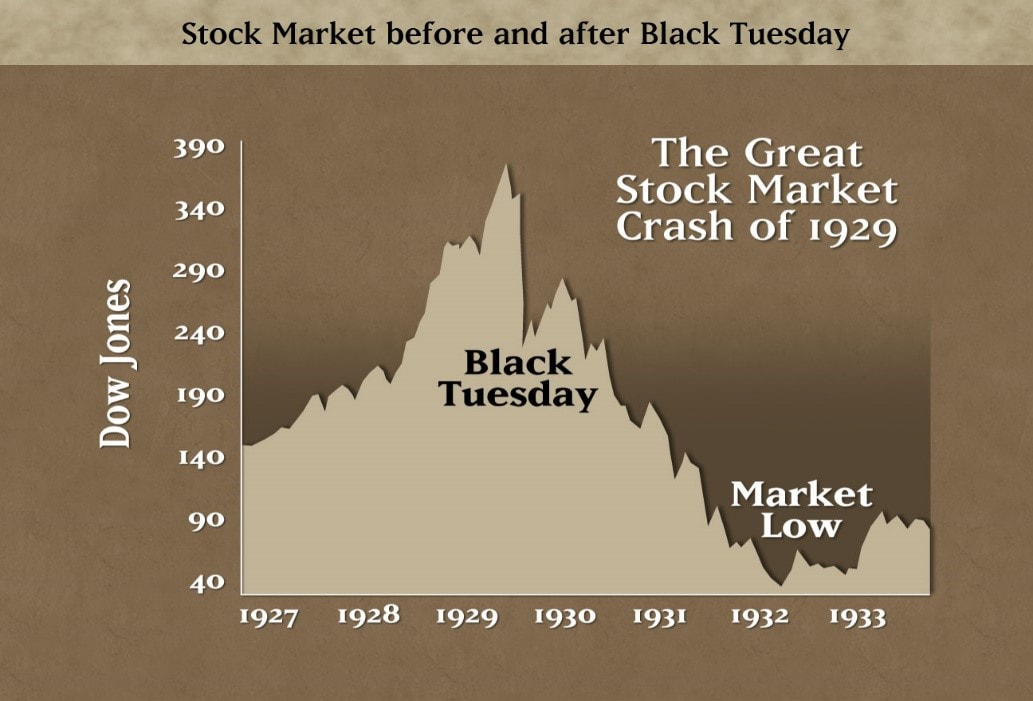 However, the stock market doesn’t always work how we imagine. Sometimes daily movements in the share market have no observable impact on the economy. For instance, think about the stock market crash of 1987. The UK was in fear that the crash would ultimately cause a recession. So it cut interest rates, which surprisingly caused an economic boom. Even the collapse in share prices from 2000 to 2004 in the UK did not reflect any serious problem for its real economy. There is a long-standing debate among economists about whether or not the stock markets influence the economy in real. Though there are many arguments on this topic, we can try to sum-up some effects of the stock market on the economy and individual study which conclude that the change in share prices always cannot be a key factor to judge the situation of the economy. Some economic effects of the stock market:
On the other hand, this increase in share prices indicates a bull stock market, it may not affect the whole economy much as only rich consumers can invest more in this situation. And even if there is a downfall in prices, they can bear short-term losses.
Though stock markets have some effects on the individual consumers and businesses and as a whole of the economy, it’s not the only factor to affect the economy. Fiscal policy decisions can also be important factors. For instance, large budget deficits can eliminate government investments slow down the economy. Interest rates can also affect it because rising rates indicate higher borrowing costs, restraining economic growth. On the other hand, falling interest rates can stimulate the growth of the economy. The stock market is sometimes very tricky and complicated. Though it is commonly believed that a rising or bull stock market is indicative of a progressive economy, it’s not always true. At times, any inverse situation can also occur. How the stock market influences the economy is a matter of concern after the reckless lending exploits of certain monetary institutions led to the economic recession that occurred just before the turn of the decade. However, the effects of stock on the real economy are still uncertain and need further comprehensive analysis.
12 Comments
6/22/2022 02:37:46 pm
Experience world class online Stock Market brokerage services. The best share market stock brokerage and securities house in Bangladesh. We provide the best customer service with latest technologies and low commission rate.
Reply
6/22/2022 02:41:11 pm
This blog are very helpful to gain good knowledge about stock market.
Reply
7/26/2022 05:36:47 pm
Experience world class online stock market brokerage service in Bangladesh. Midway Securities Ltd. is one of the oldest, most prominent and well recognized Securities Brokerage house in the dhaka stock exchange, providing client service with success since 1975. In recent times our company has grown into a promising name for innovative and multidimensional brokerage services, pioneering the age of full fledged online share trading. Helping you invest your money is a job we take very seriously.
Reply
8/16/2022 03:26:06 am
I agree, by far Gold is still the best material investment you can have as of today. Cryptos and other digital commodities were in but I still belive that having something that you can hold for long time is still worth it.
Reply
Excellent post. I LOVE this article! We are a team of expert designers who possess expertise in producing great quality bank statement PDF, bank statements PDF services, paystubs PDF, utility bills PDF and tax returns PDF using your provided documents or creating our own. Because we help our customers to use the bank statements PDF services for educations and entertainment purposes.
Reply
9/29/2022 02:40:56 pm
At times of uncertainty in the stock market, these bond markets offer a better return. However, at times bond markets are the reason for the fall in share prices. Thank you for taking the time to write a great post!
Reply
11/1/2022 11:42:22 pm
And they prefer to spend this money where there is a chance to generate more money. Hence, they find the stock market to be the best place for this purpose. Thank you for taking the time to write a great post!
Reply
10/12/2023 07:33:25 pm
Thanks for your post.
Reply
10/14/2023 08:18:53 pm
Reply
2/16/2024 02:22:09 am
Reply
Leave a Reply. |
Send your articles to: |


